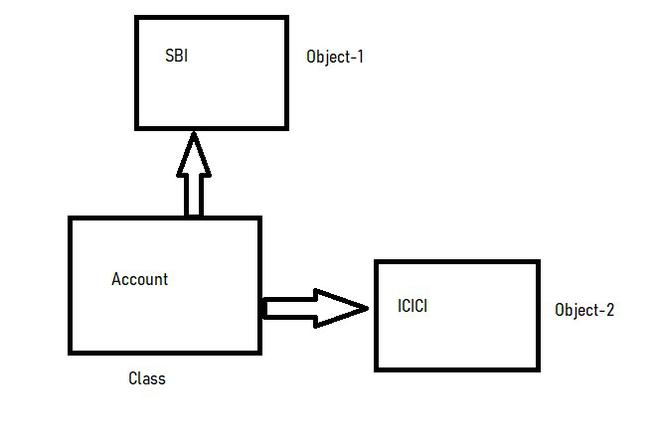
Class is a detailed description, the definition, and the template of what an object will be. But it is not the object itself. Also, what we call, a class is the building block that leads to Object-Oriented Programming. It is a user-defined data type, that holds its own data members and member functions, which can be accessed and used by creating an instance of that class. It is the blueprint of any object. Once we have written a class and defined it, we can use it to create as many objects based on that class as we want. In Java , the class contains fields, constructors, and methods. For example, consider the Class of Accounts . There may be many accounts with different names and types , but all of them will share some common properties, as all of them will have some common attributes like balance, account holder name , etc. So here, the Account is the class.
Object is an instance of a class. All data members and member functions of the class can be accessed with the help of objects. When a class is defined, no memory is allocated, but memory is allocated when it is instantiated (i.e. an object is created). For Example, considering the objects for the class Account are SBI Account , ICICI account , etc.

Fig-1: Pic Descriptions Class and object

Fig-2: Class Diagram To Understand Class and Object